Injury or damage caused by any force acting on the human body from outside is called trauma. In the discipline of orthopedics and traumatology, physical injuries that occur in the musculoskeletal system are handled under the heading of trauma. Apart from the reasons that every person can encounter frequently in daily life such as falling, hitting, sprain, these injuries can occur due to many different reasons such as traffic accidents (inside or outside of the vehicle), home and work accidents, sports injuries, firearm injuries and natural disasters (earthquake, getting trapped under debris, etc.).
Depending on the severity of the trauma, the damage can range from a simple soft tissue crush to comminuted fractures in large bones and even limb (extremity) ruptures. Generally high-energy injuries are the cause of trauma in young individuals, but musculoskeletal trauma can also occur with low-energy simple injuries in older people with poor bone quality.
Orthopedic injuries that may occur as a result of trauma can occur in isolation or in combination as fractures, joint dislocations, bone and soft tissue (muscle-tendon-ligament, vessel and nerve) injuries around the joint. If traumatic injuries are not treated appropriately, problems such as infection, limitation of joint movement and calcification, and even loss of limb (extremity) may be encountered, apart from complications such as malunion or nonunion specific to fractures.
In multiple injuries that can affect many systems, a number of problems may arise that can put the person’s life at risk. Therefore, in the treatment of a traumatized patient, it is an indisputable fact that a well-equipped and well-organized surgical center is needed. It is vital that the trauma patient is welcomed and first aided by the relevant specialist.
Non-operative (conservative) approaches and surgical methods are constantly being renewed in the treatment of fractures. In parallel with technological developments, better and more modern treatment methods that cause less additional damage to the person are being developed day by day. Regardless of the form of the injury caused by trauma, the aim of the treatment is to ensure the integrity of the body, to restore the functions of the relevant area, and to perform all these in a way that allows the person to return to his active daily life as soon as possible.
Treatment methods used in orthopedic traumatology can be listed as follows:
CONSERVATIVE (NON-SURGERY) TREATMENTS:
It generally involves fixing the traumatic area with plaster, splint or some dressing techniques. In some orthopedic injuries, the hard and long casting treatments used in the past have been replaced by semi-rigid or softer fixation methods and fixation methods that do not cause premature weight bearing and function limitation. Today, these fixation tools can be designed and produced individually. In addition, there are a number of devices that can shorten the healing time of injuries in the musculoskeletal system and that can be articulated with fixation tools (ultrasonographic stimulants, etc.).
SURGICAL TREATMENTS:
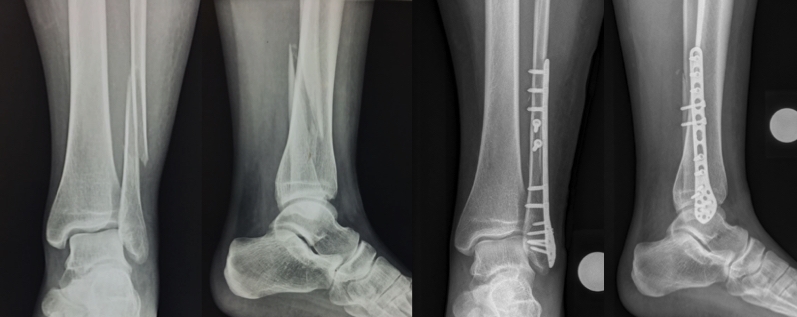
PLATE-SCREW FIXATION:
These implants, which have been used in fracture fixation since ancient times, are now manufactured from metals with high compatibility with the body. These implants, which are basically made of stainless steel and titanium, are the most basic implants of orthopedic traumatology. Many regional fractures, from a simple finger fracture to pelvis and spine fractures, can be repaired with these fixation materials.
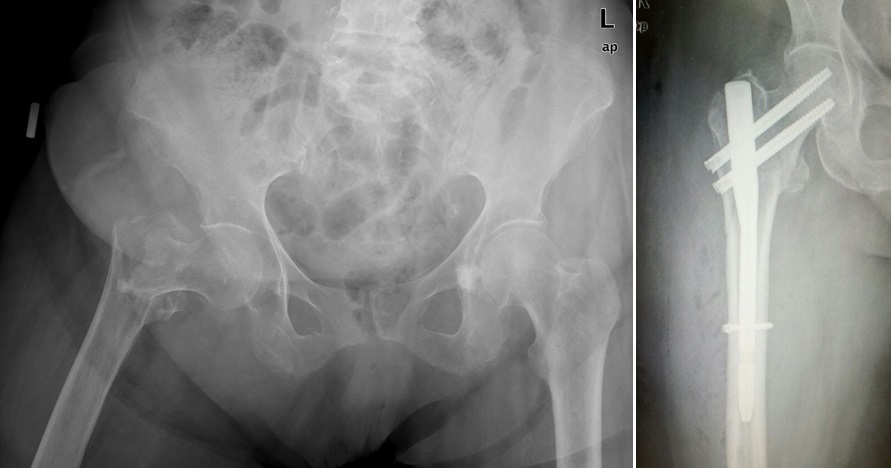
CLOSED INTRAMEDULLARY NAILING TECHNIQUE:
These are techniques applied in the majority of long bone fractures (simple-compartmental) and hip fractures in the upper (arm and forearm) and lower (thigh and leg) extremities, which do shorten fracture healing time and are performed with implants placed in the bone using small skin incisions (2-3 cm) without opening the fracture line.
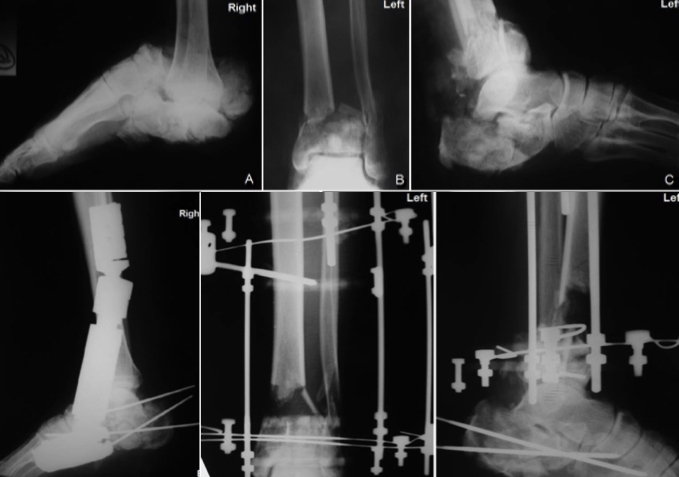
EXTERNAL FIXATOR FIXATION:
These are fixation methods that are generally used in multi-part, open fractures, which are associated with the external environment. These methods minimally disrupt the nutrition of the bone, also performing the fracture healing in a biological way.
MINOR INTERVENTION OPERATIONS WITH ARTROSCOPIC ASSISTANCE:
In some of the intra-articular fractures, this technique enables the detection of fractures without opening the joint. In this way, these techniques reduce the possibility of joint stiffness that may occur after surgery, and shorten the time to reach full function and the time needed for physical therapy (see Arthroscopic surgery).
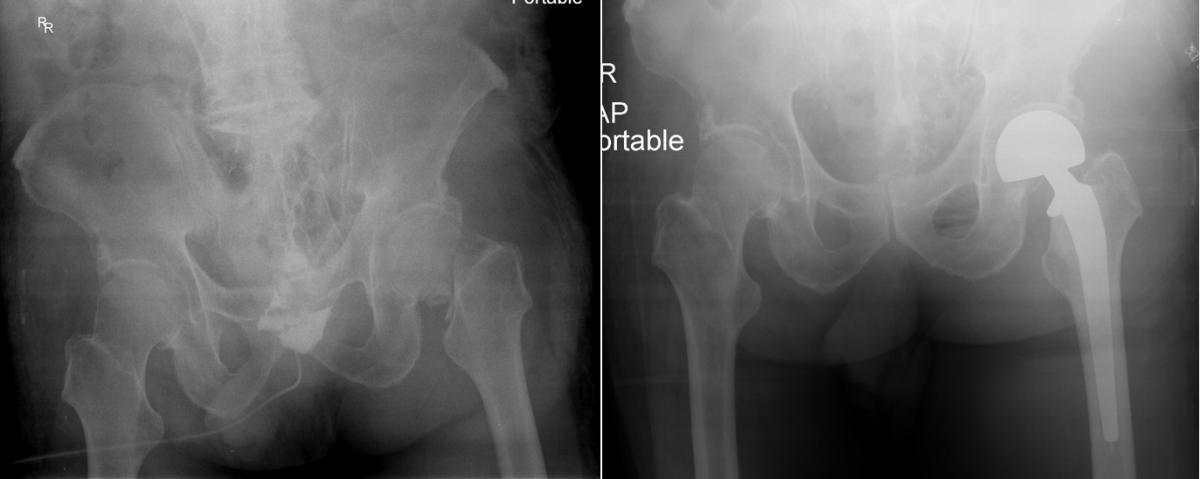
PROSTHETIC SURGERY:
It is a surgical procedure performed with partial or full joint prosthesis in elderly patients with poor bone quality, especially in hip and shoulder fractures or in fractures where the patient’s own bone is irreparably damaged.