The foot is an anatomically and biomechanically complex region in the human body, and it is an important region that hosts many bone-, joint- and soft tissue structures together with the ankle joint. In spite of that, the intense interest shown to other anatomical regions in the discipline of orthopedics&traumatology has caused this region somehow to be ignored for many years. The foot-ankle region, which carries almost all the burden of our body during daily- and sports activities, has become -with the increase in scientific knowledge- one of the important sub-branches of orthopedics & traumatology in recent years.
When it comes to foot and ankle area problems, ankle sprains, tendon/ligament problems, big toe deformities, calluses, sole and heel pain often come to mind. Considering that each foot contains 26 bones, more than 100 ligaments and 33 muscle groups, it is possible to think that the diseases of the region, which has such a complex anatomy, are much more than predicted.
The ankle is an area that contains two joints in a row. In this way, the ankle can move up and down, and it also has inward and outward mobility. The foot area, on the other hand, ensures that the bone and joint structures it contains move harmoniously and regularly together with the ankle joint via its strong ligament support and tendon anatomy. Orthopedic surgical interventions in the ankle area are often applied for degenerative diseases, ankle fractures and dislocations, sports injuries, ligament/tendon problems and cartilage injuries. Foot surgery is applied for many problems such as big toe and other little finger deformities, flat feet in children and adults, diabetic foot, rheumatological foot problems, tendon problems, heel problems, foot deformities leading to walking disorders, congenital deformities, ankle cartilage lesions, sports injuries, neurological problems, finger and nail disorders, calluses, heel fractures and related sequelae.
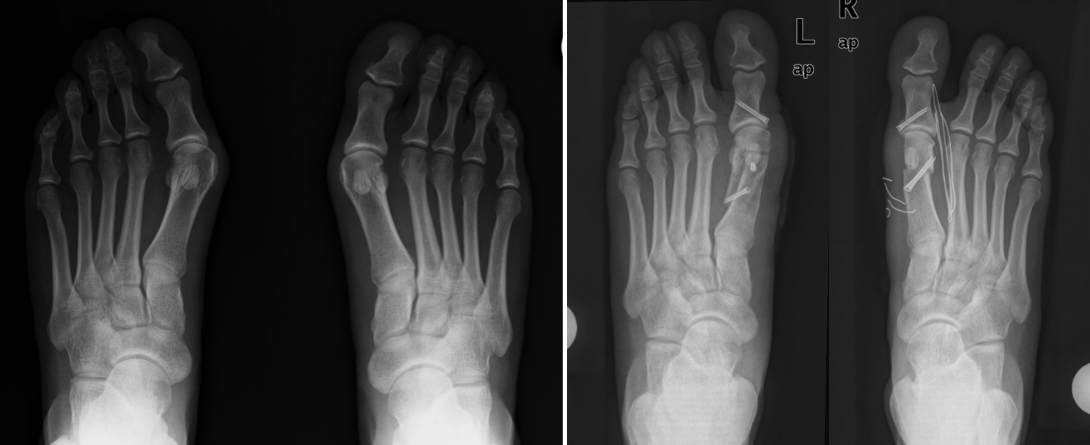
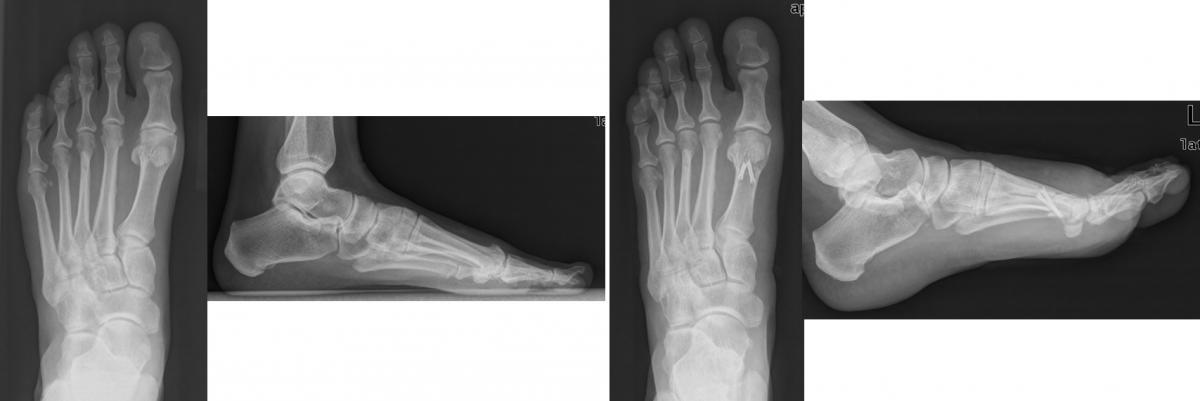
Orthopedic problems of the foot region are usually examined in three separate anatomical parts (front-middle-back). When evaluated from this point of view, common foot problems can be grouped as follows:
Forefoot disorders:
- -Hallux valgus (toe protrusion)
- -Hallux rigidus (calcification of the big toe joint)
- -Lesser toe deformities (deformities of the 2nd-4th toes)
- -Ingrown toenails
- -Morton’s neuroma
- -Diabetic foot problems
Midfoot problems:
- -Metatarsalgia (pain in the ball of the foot)
- -Pes planus-planovalgus (flat foot)
- -Adult-acquired flatfoot
- -Fractures and dislocations of the midfoot (Lisfranc injuries)
- -Stress fractures of the tarsal bones
Back foot problems:
- -Plantar fasciitis and heel spur
- -Insufficiency in ankle ligaments (instability)
- -Achilles tendon problems (tears and tendonitis)
- -Cartilage problems
- -Tarsal tunnel syndrome (nerve compression in the ankle)
- -Degenerative diseases (calcification)
- -Ankle impingement syndrome
- -Peroneal tendon problems
- -Posterior tibial tendon problems-Avascular lesions at the navicular and talar bones
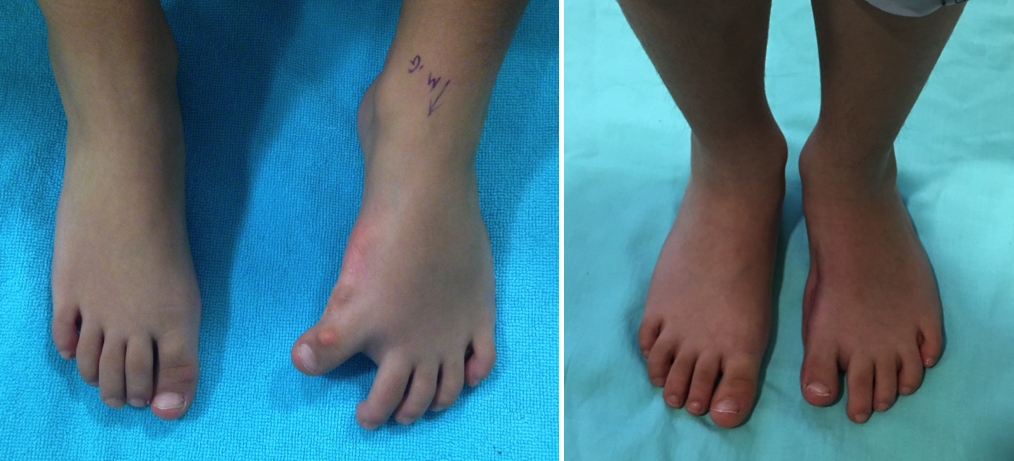
At the beginning, orthopedic problems of the foot and ankle are tried to be treated with non-surgical methods. Appropriate shoe selection, modification of daily activities, auxiliary orthoses, personalized insoles and physical therapy applications are the main forms of treatment at this stage. However, as in other orthopedic problems, surgical interventions become a priority only in the late stages. Depending on the type of orthopedic problem, surgical interventions to be performed can be open or closed (arthroscopic) interventions and their combinations.